Information on this page is for customers in
{{ town-name }}
Electrical Terminology
Electrical grid or "the grid"
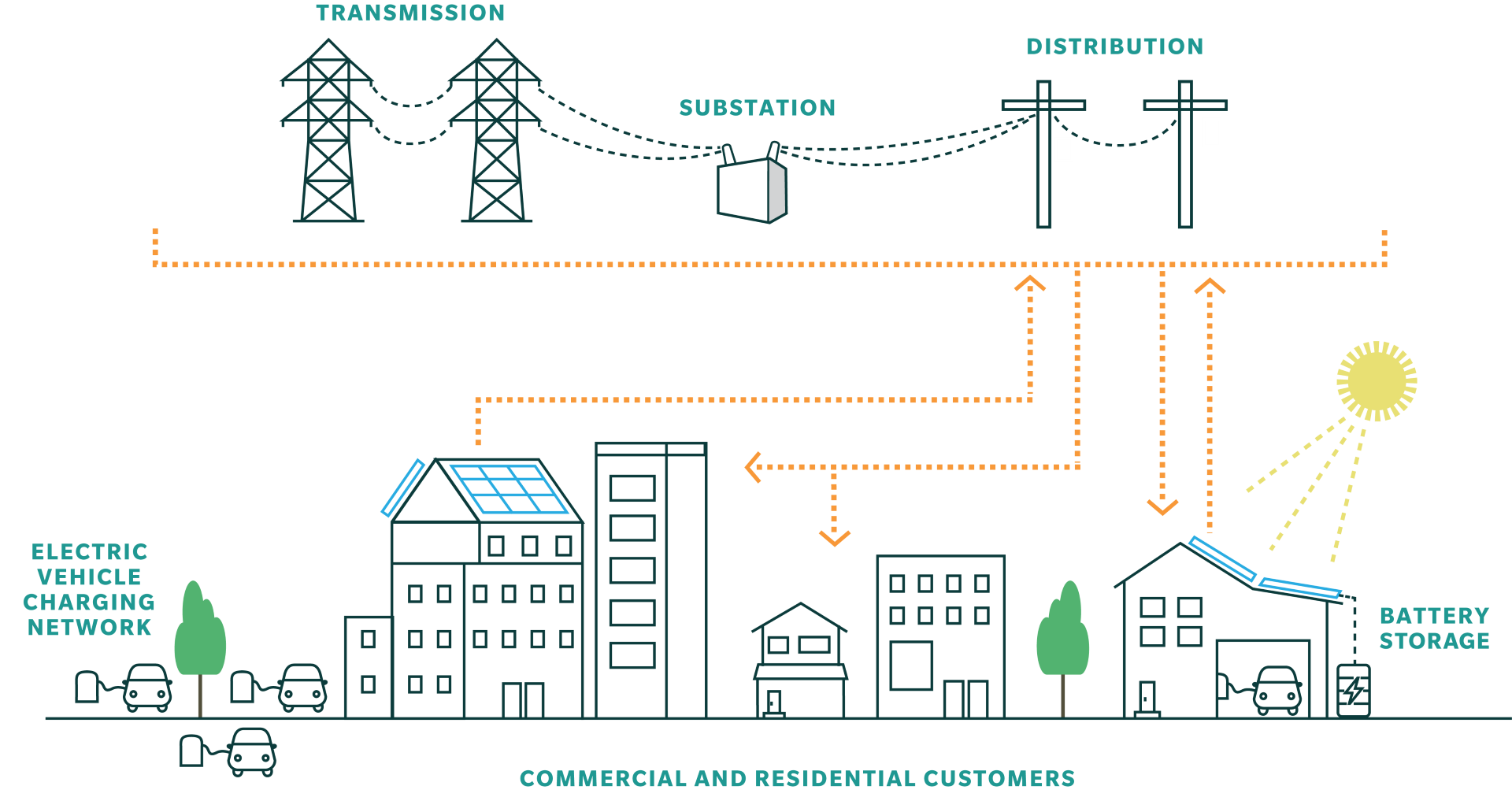
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. Large power generators are interconnected to the grid by way of high-voltage transmission lines.
All of these lines, when networked together create a type of superhighway that moves electricity from the power plants to electric substations and then to local distribution systems, which ultimately deliver it to homes and businesses. The combination of these components is what we call the U.S. electric grid.
Clean energy
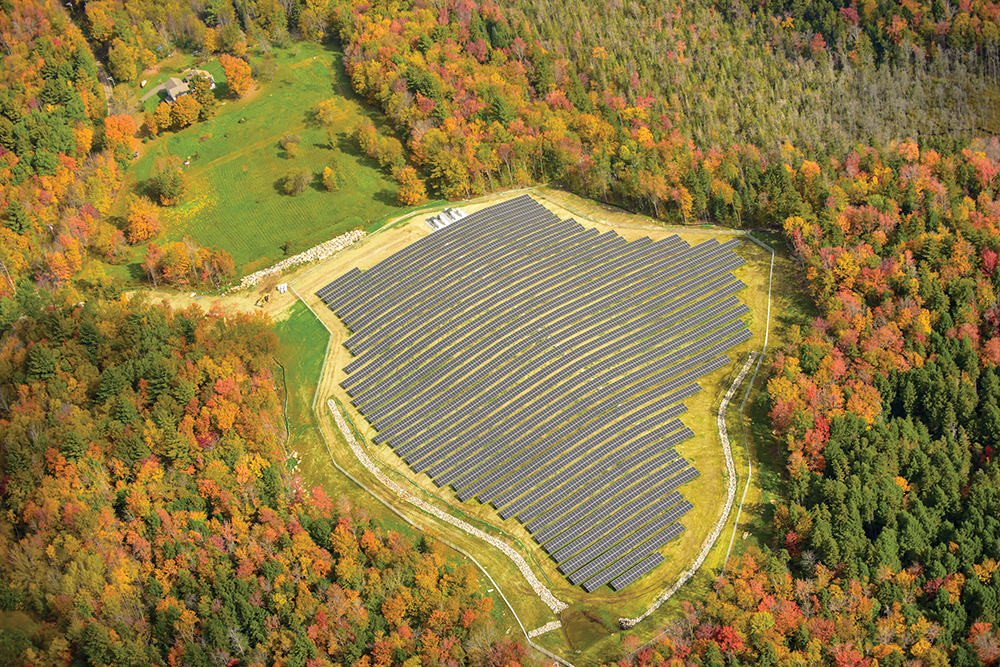

Renewable or “clean” energy is energy that is collected from natural resources that are more rapidly replenished on earth compared to fossil fuels. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water and geothermal.
Substation

A substation is part of the electric system and is a crucial piece of equipment to bring electricity to homes and businesses.
It plays a vital role in the transmission and distribution of electricity from generation sources – like offshore wind or solar farms or other electric generation stations – to end-users like homes and businesses.
It takes in high-voltage electricity from power plants and reduces the voltage so it can be safely utilized by homes and businesses. A substation is not a power plant and does not produce emissions.
Transformer
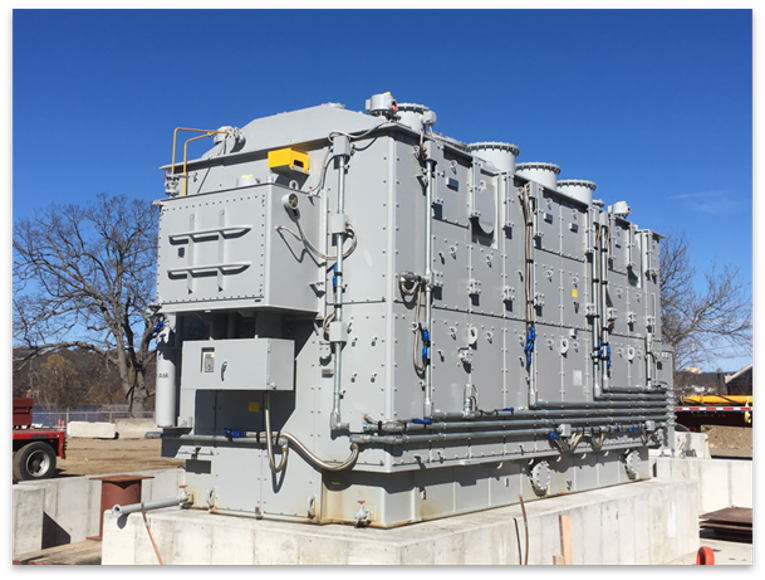

A transformer is an electrical apparatus that controls the level of voltage flowing through any point in a power grid. In a distribution system, the transformer decreases the voltage traveling through power lines to a level more suitable for residential and commercial use.
Battery energy storage system
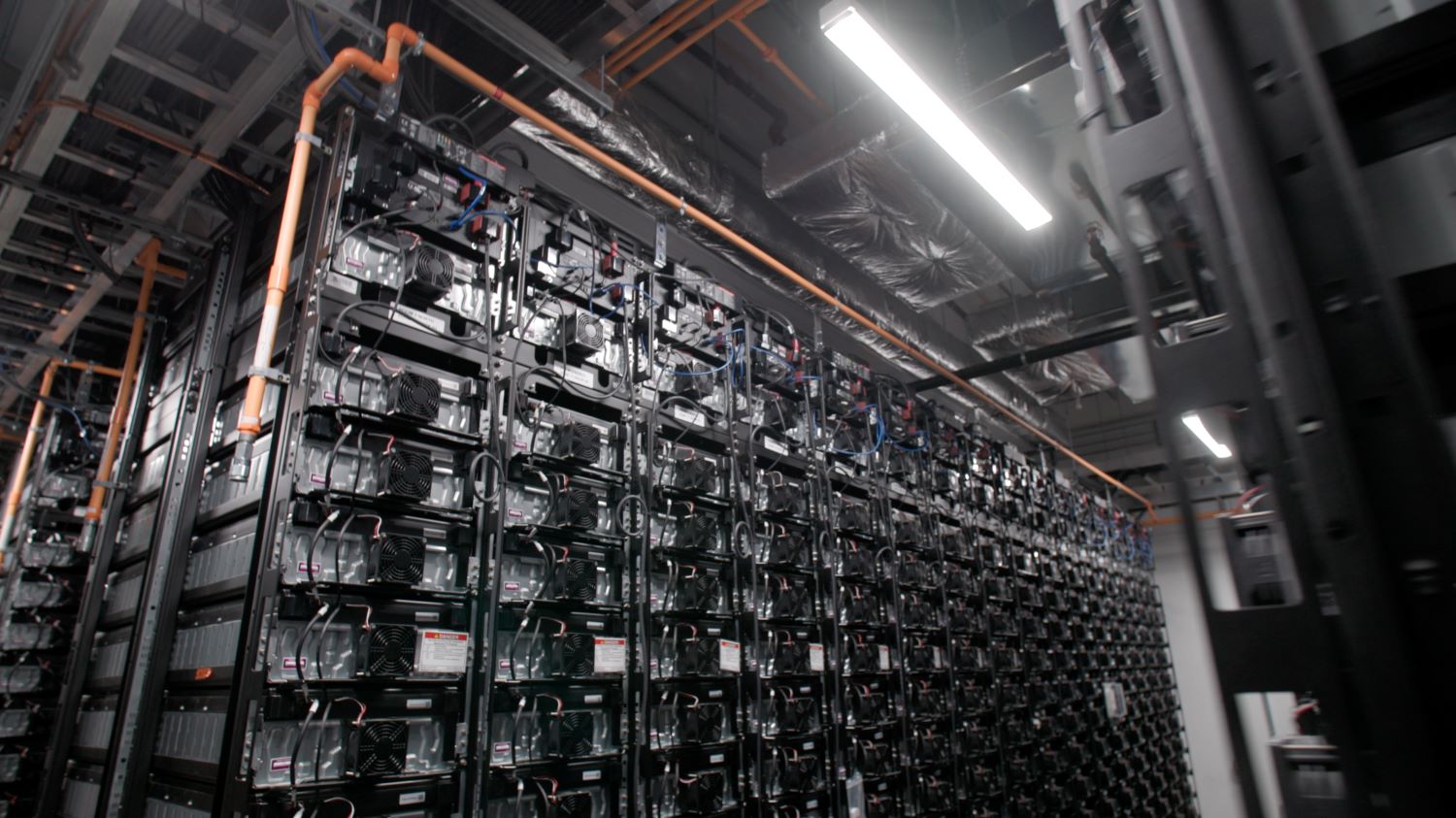

Battery storage is a technology that allows utilities to store energy for later use. A battery energy storage system (BESS) charges (or collects energy) from the grid or from remote power sources, like wind or solar farms, and then discharges that energy later to provide electricity when it’s needed.
Voltage
Voltage is the electrical property that causes an electric current to flow. Voltage is produced by a generator. Batteries also provide voltage.
Current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space.